Radiant heating system in a private house. Radiation heating system for a private and multi-apartment building. Analysis of the arguments "for" and "against"
Arrangement heating system is the most costly item in the estimate of major repairs or construction. From the correct installation and the features of all elements of this object, the operational characteristics, the costs of the owners for energy resources in the winter period depend.
The radiant heating system is gradually replacing the outdated tee wiring. This is due to a number of its advantages. How to equip such a wiring on your own, as well as what are its main features, the master must find out before starting installation.
general characteristics
Autonomous heating in a private house can be performed using various wiring. The beam system is also called the collector system. Each radiator in the building is connected to a distribution manifold. A separate pipe enters the heater. Each of them returns its own pipe to the collector. Radiators with this connection are a separate element. They don't depend on others heating appliances networks and are brought to the collector in parallel.
The collector is a general device. He is responsible for supplying the coolant to each individual circuit. If it is necessary to repair one battery, the heating system continues to operate as before. Only one radiator is cut off.
Individual heating according to the tee scheme involves a smaller number of pipes. However, installation costs pay off during the operation of the system. The positive economic effect from the use of beam wiring in a large house or cottage with two or more floors is especially pronounced.
Advantages and disadvantages
Some features are characterized by the beam wiring of the heating system. The pros and cons of such an organization must be considered before installation. The disadvantages include a larger number of pipes and fittings. This greatly increases the cost of repairs. The tee scheme is much cheaper during installation. Also, a large number of connections, if connected incorrectly, can lead to frequent system breakdowns.
However, all these shortcomings fade against the background of the advantages of the radiation organization of heating. In this case, the system quickly pays for its installation cost. The ability to regulate the heating in each room significantly reduces energy costs. When organizing such a system, many joints and surges are obtained. The master has easy access to them. Therefore, when carrying out repairs, this factor greatly facilitates the work.
The pipes of the beam system can be hidden under the floor, in the thickness of the wall or simply behind the curtains. A properly planned scheme allows you to remove unattractive communications from view. The tee scheme does not provide such an opportunity to homeowners.
System elements
Beam wiring of the heating system consists of several mandatory elements. The main one is the boiler. When calculating its power, the area of \u200b\u200bthe premises, as well as the heat loss of the building, are taken into account.
The scheme includes circulation pump. There are systems with natural circulation of the coolant. However, they are less efficient. Today, almost all radiant heating schemes incorporate a pump. It forces the heated liquid to move along the contours at a certain speed. In this way, it is possible to maintain the optimal mode of heating the room.
The collector is a distribution unit. He is responsible for the optimal nutrition of all circuits. This element may incorporate various control and shut-off equipment. The presented devices are installed in a special cabinet. This allows you to protect the equipment and hide it from prying eyes.
Circulation type
The radiant heating system of a private house can use the principle of natural or forced circulation. In the first case, the coolant is distributed through pipes and radiators by gravity. This requires the installation of pipes of large diameter. It's simple but less efficient system. It is only suitable for small one-story house which is not supplied with electricity.
AT modern construction beam systems are used in combination with a pump. It provides forced circulation of the coolant. The pump is installed on the supply or return circuit. It works with a certain power. Such a device is necessary for the heating system of a large or two-story cottage.
Due to the mass of advantages, as well as the reasonable cost of circulation pumps, today this installation option is used almost everywhere.
Design
The calculation of the radiant heating system is carried out at the design stage. To do this, on paper, you need to draw a detailed diagram with dimensions. It lists all elements. If necessary, the drawing can be ordered from a special organization.
First you need to evaluate the existing features of the premises. The rooms should not be decorated. It is best to hide the pipes in the floor under the screed. The plan also indicates the radiators, their location (on the wall under the window). The number of sections and their internal volume depend on the material of the convector, as well as the thickness of its walls. In accordance with the parameters specified by the manufacturer, the need for the volume of coolant for each battery is calculated.
Autonomous heating in a private house according to the beam scheme is characterized by some additional heat losses. The heated liquid is supplied to the batteries through pipes, the length of which will be greater than in the tee scheme. This feature must be taken into account in the calculations.
The plan shows where the pipes will be laid. Manometers, thermometers, shut-off and control valves are added to the equipment. Before installation, you should carefully consider all the elements of the main and additional equipment. The sequence of their installation is also indicated in the diagram.
Manifold selection
The radiant heating system incorporates a collector (comb). This element looks like a pipe. It has fittings for the inlet and outlet of the coolant. For a beam scheme, two types of collectors should be installed.
The first of these will be the input comb. A pump is connected to it, as well as a coolant distribution valve. It can be three- or two-way. The valve contains a thermometer. It is installed in the collector housing. The device transmits information to the valve. It opens or closes the damper, mixing hot liquid into the circuit.
The outlet collector collects the cooled coolant, which is returned to the boiler. The heater heats it up again. Additionally, a balancing flow controller can be installed on this branch pipe. The collector group ensures the stability of the system. It is responsible for optimizing and balancing the heating of the coolant in the system.
Pipe selection
Individual heating, which is mounted according to a beam scheme, requires correct selection pipes. Communications must be flexible enough to avoid the installation of a large number of connections. Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene are best suited for these purposes. Such products are sold in bays.
Polyethylene pipes, which are suitable for a radiant heating system, must have an airtight layer. When using conventional varieties, air enters the system. It leads to the development of corrosion of metal elements, the rapid failure of equipment.
¾ inch pipes are used to connect the collector to the boiler. Radiators can be connected to the comb with ½ inch communications. This is possible if a circulation pump is used in the system. Otherwise, the diameter of the pipes may be larger.
Mounting Features
A radiant heating system can be installed by the owners of a private house. To do this, it is necessary to allocate a separate room for the arrangement of the boiler room.
After installing the heater, a comb is mounted immediately after it. The equipment must be in a protective box. The collector must be freely accessible. A manometer and a thermometer are installed at the outlet of the coolant. Mayevsky crane and other safety devices allow to stabilize the pressure in the system.
Shut-off valves allow, if necessary, to carry out preventive maintenance or repair of equipment. After installation, the equipment is checked. If everything is normal, the pipes are poured into the screed.
User Reviews
The radiant heating system, user reviews of which are presented in large numbers, is considered today one of the best principles for organizing communications, in their opinion. It reduces the cost of energy bills cold period. The effectiveness of such a scheme will be high if the construction of the house was carried out in accordance with all building codes.
If the owners used quality materials for insulation, there are no large heat losses in their house, the collector circuit allows you to optimize energy costs. Otherwise, such a system will not be effective. The tangible effect of the use of such a scheme is determined in large or two-story houses.
Having considered what a radiant heating system is, as well as the features of its organization, each owner of a private house will be able to equip such a scheme on their own.
fb.ru
Features of the collector wiring device
The principle of operation of the system is based on the separation of coolant flows. This is possible thanks to the installation of the collector. From it to the heating devices are independent pipe circuits (“beams”, “branches”, “loops”). The collector itself is a piece of pipe with branch pipes, of which one is the inlet. When installing temperature control equipment, you can achieve different temperature conditions in different rooms Houses. To do this, put valves with electric actuators. They regulate the intensity of the coolant supply. If the pressure in the system exceeds the allowable, then the air can be bled through special air valves.
Pipes leading from the collector to the heaters are usually laid in the floor screed. Options - disguise under skirting boards, behind a suspended ceiling structure. Almost no elements remain in sight, which has a positive effect on appearance rooms. The system uses pipes of the same diameter, they form "loops" from the collectors to the radiators. If necessary, a separate circuit can be disconnected and repaired without stopping the operation of the entire heating system.
Where is the best place to use the beam wiring of the heating system
This type of wiring is ideal for houses with several floors. Also, the beam system is installed in large houses with many rooms. It is quite difficult to install, it is necessary to equip the collectors on each floor, and the structural elements have to be mounted in a cement screed. Difficulties and high cost of installation pay off:
- the collector system has good heat transfer;
- no unnecessary losses of thermal energy;
- all equipment works more efficiently than with a tee installation.
What elements does the collection system consist of?
Boiler. Centerpiece, as in any other heating system, is a boiler. From it, the heated coolant is fed through pipes to the radiators. When choosing a heat generator, it is important to correctly calculate the required power, taking into account the heat loss of a particular house.
Pump. It is installed for forced circulation of water in the system. When choosing a pump, you need to focus on the dimensions of the pipes, materials and features of the heating devices. An important parameter when choosing a pump is the speed of pumping the coolant, in second place in importance is the power of the device.
Collector. For external resemblance to a comb, a structural element is also called a comb. This is a distribution system that is installed to transfer the coolant to all heating devices. Shut-off and control devices can be installed on the collector, which will allow you to control the coolant flow in each "loop". If equipping the comb automatic systems ventilation and thermostats, you can achieve maximum heating performance with minimum energy consumption.
collector cabinets. These are structures in which combs are installed. There are the most different models- from the simplest hanging boxes to "invisible" cabinets that are built into the walls and "masked" finishing materials so that they become almost invisible in the interior. The collector cabinets contain the most important elements of the beam system - the comb itself, valves, pipelines.
What to look for when choosing a collector (comb)
Combs may vary depending on the material from which they are made, the number of contours, the type additional elements. Devices are made from the following materials:
- steel;
- copper;
- brass;
- polymers.
Contours can be 2-12 depending on the model. The peculiarity of the comb is that, if necessary, additional contours can be added.
By design, collectors are:
- simple, consisting only of basic elements, without any additional control equipment;
- advanced, in which the manufacturer installs automation, sensors and other additional elements.
Simple designs are ordinary tubes with branches and connecting holes. Advanced ones can have temperature and pressure sensors, thermostats, electronic valves, mixers.
When choosing a collector, you should decide on the material and design of the devices, as well as take into account the following nuances:
- throughput of the comb;
- the number of contours;
- the maximum allowable pressure at which the collector is able to work;
- power consumption for the operation of the device;
- reputation of the manufacturer in the market heating equipment.
Beam wiring of a heating system with natural and forced circulation
Collector heating uses predominantly forced circulation, but there are cases when it makes sense not to spend money on installing additional equipment and equip a gravity system.
and installation of heating with natural circulation, large-diameter pipes and an expansion tank are used. It must be installed at the highest point of the building. The absence of pumps, automation and other expensive elements can significantly save on the arrangement of heating. This is a good option for country cottages. Such a system is less productive than forced circulation, but much cheaper. It can be equipped in houses that are not connected to the mains.
Equipment for forced circulation of the coolant costs a significant amount. A decade ago, many homeowners simply could not afford it. But every year, structural elements are becoming more accessible and therefore more popular. To equip the system, it is required to install not only a circulation pump, but also automation, shut-off, control valves, consisting of sensors, taps, thermal heads, air vents. It is easier to design heating: less importance is attached to the geometry of the premises, the system works perfectly regardless of the length of the “beams” and the hydraulic resistance of the pipeline.
Is it worth it to do the collector wiring of heating
Let's start with the disadvantages. They must be taken into account when deciding on the choice of the type of wiring for heating pipes. The collector system is considered expensive due to the material consumption. In addition, you need to find a place to arrange cabinets, which is sometimes difficult. If the costs and the need to allocate space for collectors are not scary, then the homeowner receives the following benefits:
- Stable operation of the heating system. The equipment is not exposed to water hammer, which increases the life of the radiators.
- Simplified design. The system uses pipes of the same diameter, which eliminates unnecessary calculations.
- Convenient repair. If damage appears in any area, this circuit is simply turned off and troubleshooting. The rest of the "rays" work in the same mode, an acceptable temperature is maintained in the house.
- Concealed installation. Pipes are located in the floors, walls or ceilings, and the comb and automation are in the manifold cabinet. Heating elements do not spoil the interior.
Whether to opt for beam wiring or prefer the good old tee - it's up to you. Weigh the advantages and disadvantages, calculate the installation costs of different types of systems and start designing. Warmth for your home!
teploguru.ru
Collector (radiant) heating system of a private house
The distributive collector for a water heat-insulated floor assy.
Design and principle of operation
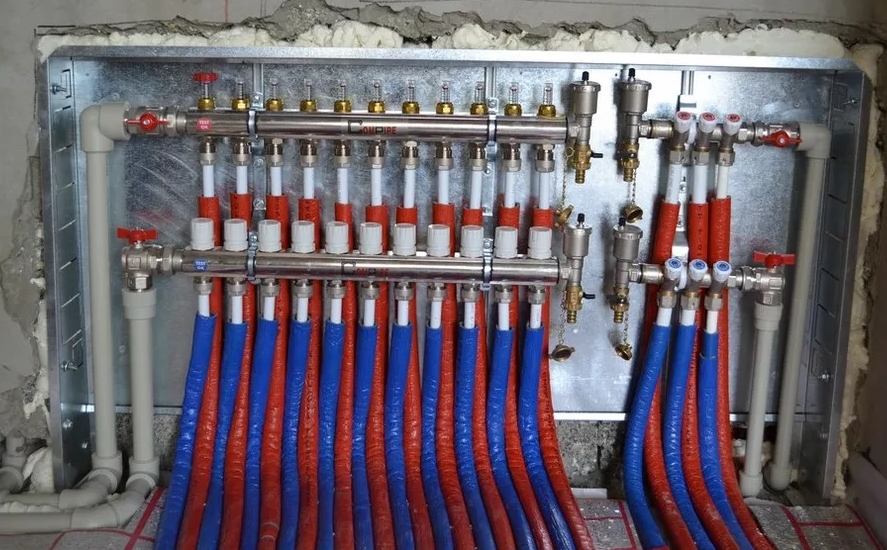
One of the main elements of the collector heating system is a collector (comb, collector block), which distributes the coolant coming from the boiler over several circuits. The number of circuits corresponds to the number of taps on the manifold, how many taps on the manifold, so many radiators in the house.
The collector allows you to evenly distribute the coolant over each heating device, so that all radiators heat up to the same temperature. Uniform heating is ensured by the fact that each radiator has its own supply and return lines.
The design of the collector consists of several outlets and one inlet/outlet through which the coolant enters/returns from/to the heat source. Often the distribution manifold is equipped with a circulation pump, an automatic air vent, flow meters and thermostats.
Manifold cabinet application
When installing a radiant heating system in a private house, it is recommended to place the collector itself, the circulation pump, shut-off and control valves in a collector cabinet, which hides equipment and numerous pipes and gives the room a more aesthetic appearance. In addition, it allows you to protect the equipment from external mechanical stress. Pipes are led out through the lower, open part of the cabinet. The manifold cabinet is installed in the same place as the individual manifold, i.e. mounted on the wall, if possible, in the center of the house.

Distribution cabinet with comb, Wilo circulation pump, thermostats and electrical part…
Note! Often, when installing a collector heating system, it is not a factory collector that is used, but a self-made one made by oneself. As a rule, polypropylene tees are used for its manufacture, which are connected to each other using short segments. polypropylene pipe suitable diameter. The result is a collector that performs exactly the same role as the factory one. The only drawback of a home-made collector that is not critical for radiator heating is the additional hydraulic resistance, which is formed due to an uneven inner surface (unequal internal section of the tee and pipe segments).
For the above reason, home-made collectors are not recommended for use when installing the external circuit of a geothermal heat pump, because for geothermal systems the most important moment are the hydraulic characteristics of the system, the slightest decrease in which can lead to a decrease in the power of the heat pump.
In a collector-beam heating system, the most common material for a pipeline laid from a distribution manifold to heating devices is 16 mm metal-plastic. Metal-plastic pipes bend, they are easy to lay under the floor.
If, after the pressure testing of the system, the metal-plastic pipes are filled with a concrete screed, they must be wrapped in thermal insulation, up to the collector itself. This will avoid their damage during thermal expansion, because. pipes, expanding, will "rub" on the insulation, and not on the edge of the screed.
Important! The pipeline should not be laid through doorways, otherwise, during the installation of the threshold of an interior door, the pipe may be accidentally damaged during drilling. If the pipeline is laid through a load-bearing wall in a new house (which will shrink later), then the hole in the wall must be equipped with a sleeve that will protect the pipeline from damage.

Scheme of the collector heating system of a private house.
Advantages of a collector heating system
Fast, uniform heating of all radiators. Each heater has its own supply pipeline, so that all radiators receive a coolant with the same temperature.
Aesthetics. In most cases, the wiring of the collector radiant heating system is mounted under the floor, so only the radiators themselves and short sections of the supply and return pipelines protruding from under the floor are visible in the room.
Ease of troubleshooting. If one of the radiators leaked, the supply or return line was accidentally damaged, or there were problems with the fittings, then to carry out repair work, it is enough to shut off the coolant supply to the problem area on the distribution manifold. At the same time, only one radiator stops working, all other elements of the system continue to function.
Possibility to adjust/switch off the temperature in individual rooms. If no one permanently lives in some rooms of the house, and for example, guests come once a month, then during the absence of guests, a minimum temperature of 10-15 ° C can be set in such rooms so as not to freeze the system. Thus, there is no need to heat the "extra" coolant.

Distribution manifold with Wilo circulation pump.
disadvantages
High price. The cost of a collector heating system includes a large number of pipes (each radiator has its own supply and return), as well as the collector itself and the collector cabinet.
High heating costs during operation. Due to the many pipes, the volume of coolant in the collector-beam heating system is larger than in the two-pipe system, which does not save on heating. The more coolant, the more fuel is required to heat it.
Video
heating-guide.com
Beam scheme of heating distribution in a private house
A radiant heating system is also called a collector heating system. This is due to the fact that the distribution of the coolant is carried out by special combs (collectors), which directly or through mixing unit connected to the boiler. There are many expensive elements in this scheme, so this pleasure is not cheap. But sometimes, if you have a large house with several floors, installing radiant heating is the only possible option so sometimes you don't have to choose.
What is a radiant heating system
 In a conventional heating system, the coolant enters the supply line from the boiler and passes through all the heat exchangers in turn. The radiant heating system is different in that the water from the boiler first enters the distribution comb, and then to each heater. This comb is called a collector. The same thing happens with the return flow, which first comes to the collector, and then to the boiler (see How to install a solid fuel boiler, piping).
In a conventional heating system, the coolant enters the supply line from the boiler and passes through all the heat exchangers in turn. The radiant heating system is different in that the water from the boiler first enters the distribution comb, and then to each heater. This comb is called a collector. The same thing happens with the return flow, which first comes to the collector, and then to the boiler (see How to install a solid fuel boiler, piping).
The peculiarity is that from the collector to each battery there is a separate ring (two pipes - supply and return), which can be adjusted or turned off independently of the others. In this case, all manipulations are carried out through the collector box.
Radiant heating is ideal for big houses or apartments. In such a system, water with the same temperature comes to all heat exchangers - a slight difference may be due to different lengths of the rings. In addition, you can combine different types heating (conventional batteries and underfloor heating).
What pipes can be used for wiring the circuit
In the radiant heating system of a private house and apartment, it is customary to use only polymer pipes:
- metal-plastic;
- polypropylene;
- polyethylene.
Most installers prefer cross-linked polyethylene (PEX). Such pipes are most often red in color, they are not reinforced with foil, and in order to reduce the degree of thermal expansion of polyethylene, this material is cross-linked.
Crosslinking is a chemical process that increases the number of bonds between polyethylene molecules. Due to this, the material becomes stronger, while remaining flexible.
PEX pipes have 100% shape memory, which means that they always tend to return to their original position if you bend them. Therefore, special attention must be paid to fasteners. Pipes are sold in bays, which is very convenient, since a single piece of the line can be laid from the collector to the heat exchanger. This is important, because the installation is always carried out by a hidden method. Where necessary, the pipes are connected with press fittings. The connection reliability is very high.
Rules for installing radiant heating
 As a rule, pipes are laid in the floor screed. To reduce heat loss and leave some room for thermal expansion, polyethylene foam shirts are put on the lines - this is such a heater. During laying, you need to try to ensure that communications go in groups. So you will know exactly where the pipes are, so as not to break them in further work, for example, if you need to drill holes for attaching a ladder or installing a toilet.
As a rule, pipes are laid in the floor screed. To reduce heat loss and leave some room for thermal expansion, polyethylene foam shirts are put on the lines - this is such a heater. During laying, you need to try to ensure that communications go in groups. So you will know exactly where the pipes are, so as not to break them in further work, for example, if you need to drill holes for attaching a ladder or installing a toilet.
There are no special difficulties in laying pipes. You simply lead the ring to the radiator installation site. For such heating systems, you need to buy batteries with bottom connection. Literally 10 cm of pipe will come out of the screed. Everything looks very neat.
What should be in the collector box
You can place the collector box in any convenient place. Pipes from each battery and from the boiler stretch into it. Two combs are installed in the collector box - one for the supply, the second for the return. If necessary, there may be several pairs of combs. For example, the first distributes the coolant through the batteries, and the second through the warm floors.
 In the collector comb there are holes for piping, and there are holes for installing equipment:
In the collector comb there are holes for piping, and there are holes for installing equipment:
- flow meters;
- servo drives;
- air vents: their task is simple - to remove air plugs.
A flow meter is a device that can be used to adjust the hydraulic resistance of each branch of the circuit. It is installed on the feed comb. Flowmeters can be omitted if all rings are the same length, but this is extremely rare. Without balancing, the heating system will not work as it should. Some branches may be left without coolant.
Servo - electrical appliance, which blocks the supply of coolant to the ring (or vice versa), depending on the readings of the temperature sensors installed in each room. The temperature sensor and the servo are connected by wires. Also, a special unit can be installed in the collector box, which receives a radio signal from the thermostat and transmits it via wires to the servo.
All solid fuel gas generating boilers operate on the principle of afterburning pyrolysis gases.
The standard scheme for connecting the Galan boiler is no different from the binding of heating elements.
There are no moving parts in a servo. A polymer capsule is installed there, which contains the working substance. A copper wire is wound around the capsule. When current is supplied to the winding, it heats the working substance. As a result, thermal expansion occurs, the capsule increases in volume and blocks the flow.
In the beam scheme of the heating system for underfloor heating, in addition to all of the above, a mixing unit is installed in front of the collector. It lowers the flow temperature by mixing the return flow into it. As you know, in low-temperature systems, water should not be hotter than 40 degrees.
Advantages and disadvantages of the beam scheme
Let's start with the disadvantages of the radiant heating scheme. It is only one and lies in the high price of equipment. A good collector, like all other components, is expensive. The wiring will require more pipes than in simple systems, in addition, they still need to be insulated.
The use of solar systems will make it possible to convert the energy of the sun into thermal energy.
If you live in a high-rise building, then sealing the panel seams will significantly reduce heat loss.
But by spending money, you get the following benefits:
- pipes are laid in a hidden way and are not visible;
- practically no connections;
- the ability to adjust the hydraulic resistance of each ring separately.
In addition, there is an opportunity to introduce new technologies. For example, you can control the temperature in each room from your smartphone or computer.
findings
As you already understood, beam wiring is not cheap. Such schemes are mainly used in large cottages. For a private house, and even more so an apartment, you can find options that are much more budgetary. Thus, if circumstances do not force you, then the collector wiring can be completely replaced with a conventional two-pipe one.
utepleniedoma.com
Perimetric or radial wiring of the heating system: what to choose?

Being a variety of methods for laying heating pipes of two-pipe horizontal systems of modern apartment buildings and private houses, beam wiring of the heating system has a number of undeniable advantages. Each circuit of the system with such piping is separately connected to the heating manifold, which allows you to set an individual operating mode for it that meets the criterion of comfort for a person in a particular area of \u200b\u200bthe room.
Heating pipes laid in the thickness concrete screed or under a wooden floor on joists, should be reliable, eliminating (or minimizing) the possibility of leaks, degradation of capacity and other malfunctions.
Wiring diagrams of modern horizontal heating systems
Modern multi-apartment residential buildings and private cottages of any number of storeys are increasingly equipped with horizontal heating systems. A necessary element of such a scheme is one or more (in an apartment building - in each entrance) vertical two-pipe risers with branches / inputs to separate rooms / apartments on each floor. Further laying of pipelines is carried out in a "horizontal" way.
Arranging such systems, builders invariably face the problem of the difficulty of laying heating pipes to radiators. The pipelines of vertical systems, laid along the walls from top to bottom, did not particularly interfere with the residents. Horizontal pipes, laid openly along the walls, become a factor interfering with the normal process of operating the premises, they do not fit well into their interiors. Therefore apply various ways their horizontal hidden laying.
Branched dead-end wiring diagram with pipes in the screed

Piping layout with a branched dead-end scheme.
The minimum pipe lengths and hydraulic resistances of the circuit are leveled by the mutual crossing of pipelines, leading to an increase in the thickness of the screed (each centimeter of it costs from 40 rubles / m2).
Perimeter wiring of the heating system
- Dead-end scheme with pipelines in the screed or under the plinth.

Piping layout for a two-pipe dead-end system.
The absence of crossing pipes in the scheme is leveled by the need to make holes in the walls (in the above scheme, you need to drill five holes).
- Piping layout according to the scheme with associated water movement (Tichelman scheme).

Piping layout according to the Tichelman scheme.
Here, the first radiator of the heating circuit has the shortest length of the "supply" and the largest length of the "return", the last radiator - vice versa. The hydraulic resistance experienced by the coolant when flowing around the devices of the circuit is constant, which makes it possible to balance any number of radiators in a branch.
Collector-beam wiring of the heating system

Piping layout for a collector-beam system.
The prevalence of this scheme is constantly growing. The pipes here are laid in the floor screed in pairs (“supply” plus “return”), approaching each radiator from the collectors (respectively, “supply” and “return”). The advantage of the scheme is ease of installation (no crossing of pipes and wall holes). The disadvantage is the increased costs due to the large consumption of pipes and additional costs for collectors.
An additional advantage of the beam scheme is the use of pipes of small diameters. An apartment (floor of a private house) will require the use of pipes d = 25 and d = 32 mm for the perimeter wiring diagram. Accordingly, the thickness of the screed, the diameter of the tees that connect the radiators will increase. The cost of such an element is commensurate with the price of a pipe.
The use of beam wiring, which increases the length of the pipes, gives the ultimate benefit by reducing their diameter.
General requirements for the installation of beam wiring
With collector-beam wiring, the method of laying pipes in the floor in a screed is common, the thickness of which is 50-80 mm. Plywood is laid on top, covered with finishing flooring(parquet, linoleum). Such a thickness of the screed is quite sufficient for the free "embedding" of the intra-apartment (intra-house) radiant wiring of the heating system. It is possible to lay pipes outside along the walls under decorative plinths, which inevitably increases the length of the pipelines. Known options for laying pipes for beam wiring in the space of a false (suspended) ceiling, in strobes.

Connecting radiators with a collector-beam scheme.
Metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene pipes (PEX-pipes) are used, laid in a corrugated pipe or in thermal insulation. Unconditional advantage here possess PEX-pipes. According to SNiP, only inextricable joints can be “embedded” in concrete. PEX-pipes are connected by means of tension fittings related to inextricable connections. Metal-plastic pipes use compression fittings with union nuts. To “monolichize” them means to violate the SNiP. Each detachable pipe connection must be accessible for maintenance (tightening).
Even without fittings, not every metal-plastic pipe is uniquely suitable for laying in a floor screed. Manufacturers' products suffer from a serious defect: layers of aluminum and polyethylene delaminate under the influence of repeatedly changing coolant temperature. After all, metal and plastic have different coefficients of volumetric expansion. Therefore, the adhesive connecting them should be:
- internally strong (cohesive);
- adhesive to aluminum and polyethylene;
- flexible;
- elastic;
- heat resistant.
Not all adhesive compositions of even well-known European manufacturers of metal-plastic pipes satisfy these requirements, which delaminate over time, the inner layer of polyethylene in such a pipe “collapses”, reducing its cross section. The normal operation of the system is disrupted, and it is almost impossible to find the location of the malfunction - they usually “sin” for malfunctions of thermostats, pumps and other products with moving parts.
In the light of the foregoing, we recommend that readers pay attention to VALTEC metal-plastic pipes, which use the American DSM adhesive, which ensures the strength of the metal / plastic connection, adhesion and the complete absence of delaminations.
Collector cabinets and blocks
In an apartment with horizontal radiant heating distribution (on the floors of private houses), distribution manifolds (supply and "return") are arranged, collecting all supply and return pipelines at their outlets. They are placed in metal cabinets of a special design, often built into the partitions of bathrooms and opening inside them. It is also possible to install distribution manifolds in specially arranged wall niches. Often, the collector unit is combined with the heat metering unit in one collector cabinet.

Collector cabinet with heat metering unit.
Collectors can be complete, which are sections of thick pipes with outgoing nozzles, or assembled on tees. These devices can be:
- plastic;
- nickel-plated brass;
- copper;
- stainless steel.
Many well-known manufacturers of heating equipment (VALTEC, etc.) produce ready-made manifold blocks that combine supply and return manifolds, manual adjustment valves (on the supply manifold), thermostatic valves (on the return manifold), automatic air vents, drain valves and mounting brackets.

Complete manifold block.
The task of individual adjustment of the thermal regime of each single-radiator branch of the collector-beam heating system is solved by tuning valves with built-in flow meters. The branches are obtained in different lengths, and the coolant tends to flow in the shortest way with minimal hydraulic resistance. It flows around short branches more intensively, warming up the radiators installed there more strongly.
Adjustment valves on the supply manifold change the flow rate of water (antifreeze), narrowing their conditional passages in short circuits, and expanding in long ones. Setting is a painstaking process, and the setting valve is not designed to quickly shut off or open the coolant flow along the circuits. This function is performed by thermostatic valves.
Thermal valves on the manifold - "return" - these are valves that smoothly shut off the flow manually or automatically. The radiant heating system is easily hydraulically balanced.
Combined heating piping layout
Often, not only one heating device is installed in the room, but several. It is irrational to bring a separate two-pipe loop-branch to each radiator with a collector-beam wiring. It is better to lay a separate branch to each room, which will bypass several heating devices indoors, implementing a dead-end or passing scheme.

Scheme of the combined wiring of the heating system.
Such a system is calculated as a beam system. Branches supplying several radiators with coolant are subjected to a separate calculation as dead-end or passing ones. AT modern systems radiators are equipped with thermal valves (thermostats) that can be adjusted by users to different temperatures, based on the current requirements for comfort in the room. The stability of the temperature regime in the room becomes difficult to maintain.
It turns out that it is possible to get rid of instability while simultaneously reducing the cost of connecting radiators by connecting them according to the so-called. "through circuit".

"Pass-through" scheme for connecting radiators.
The thermal valve is installed only on the first radiator in the circuit, regulating the coolant flow for all heaters connected in series. They are perceived as one radiator. Difficulties in balancing will arise with multi-section devices (10 or more sections each).
Automatic collector-beam system
The supply of coolant to radiators connected by beam wiring can be made automatically adjustable. In this case, a small-sized electromechanical servo drive is installed on the thermal valves of the return manifold (item 2 in the figure “Complete manifold block”) instead of the plastic cover for manual control (position 4 in the figure “Complete manifold block”), connected by a cable to an analog thermostat or controller. Radiators are connected to heating pipes without fittings at all (ball valves can be installed).

Thermal valve actuator dimensions.
Such a scheme has an increased capital cost, while providing an increased level of comfort. the air temperature desired by the user can be set from the control panel room thermostat, the signals of which are processed by servo drives on the thermal valves of the "return" manifold. The system can be controlled by the so-called chrono-thermostat, which provides the user with the opportunity to set a temperature control program for a week with differentiation by day of the week and time of day.
Conclusion
The heating system with collector-beam piping provides the user with the possibility of hydraulic balancing and individual adjustment of the operating modes of heating devices. Some increase in the length of the pipes with beam wiring is obviously compensated by a decrease in their diameter and ease of installation.
Features of a radiant heating system
Heating of a private house » Installation of heating » Schemes of heating systems
Beam wiring is a two-pipe system
Any heating system is a complex of heating equipment and pipes. And in this they are all similar to each other. The only difference is the wiring and wiring diagram. Let's look at the radiant heating system as the most efficient to date.
General about heating systems
There are two main types of systems - one-pipe and two-pipe. The first is a pipe to which heating devices (radiators) are connected in sequential order. good and simple circuit with one minus - the last radiator in a row is always cold.
In a two-pipe system, this cannot be, because a separate branch is suitable from the coolant supply pipe to each radiator, providing a circuit hot water. This allows you to evenly distribute heat throughout the space of the house.
Here, too, there are two subspecies:
- Scheme with parallel connection of heating devices.
- Beam (collector) scheme.
It is about the latter that we will talk. This system requires a large amount of materials. And not only pipes, but also shutoff valves, since two lines will have to be connected to each radiator at once - the coolant supply and the return. And each line must be equipped with valves - both at the inlet and at the outlet.
Why such difficulties? This simplifies repairs in the future. If needed, it will be possible to turn off one battery without touching all the heating.
Of course, the initial investment here is quite large, but such a system works much better, especially when it comes to the natural circulation of the coolant.
Design features
The most important element of such a circuit is the collector, or comb. It is a connection of pipes at one point, from which all pipelines are routed along the mains to heating devices. The simplest version of this design is a pipe, from the side of which pipes extend. Their number is equal to the number of highways or radiators. Such a pipe is very similar to a comb, which is why it is called a comb.
On the opposite side or from below, another branch pipe is installed, which is designed for the branch through which the coolant enters. By the way, the main collector pipe and the supply pipe hot water must be the same diameter. And outgoing pipes should be smaller in diameter. A prerequisite is the installation of valves or ball valves on each line.
This is what a typical collector looks like
It was the top feed manifold. There is exactly the same lower one, to which the return lines from each radiator fit. Very often, if the system uses forced circulation of the coolant, the upper and lower distributors are combined into one unit:
- First, it simplifies the design by minimizing the node size.
- Secondly, to install such a comb, you need little space.
- Thirdly, it becomes possible to effectively adjust the temperature inside the system and each heating device separately.
If the house is large enough, then you will need to break the entire heating circuit into several sections. Remember that you can not install collectors in series - only in parallel.
More recently, combs were made by hand from metal pipes required diameter. Now manufacturers of heating equipment offer a wide range of ready-made collectors that can provide an effective distribution of circuits depending on the number of heating devices. And here it is important to choose the right comb not only by the number of branches, but also by their diameter and boiler power. Therefore, some knowledge is simply necessary.
Plus, modern distributors are made from different materials. For example, from brass, stainless or tool steel, polymer textures and more. Of course, the price of each material is different, respectively, and the cost of products will be different. Therefore, each consumer is looking for what he needs. However, any kind is worthy of attention, because the quality of modern products is at the highest level.
Beam wiring: features and elements
Modern multi-apartment residential buildings and private cottages of any number of storeys are increasingly equipped with horizontal heating systems. A necessary element of such a scheme is one or more (in an apartment building - in each entrance) vertical two-pipe risers with branches / inputs to separate rooms / apartments on each floor. Further laying of pipelines is carried out in a "horizontal" way.
Arranging such systems, builders invariably face the problem of the difficulty of laying heating pipes to radiators. The pipelines of vertical systems, laid along the walls from top to bottom, did not particularly interfere with the residents. Horizontal pipes laid openly along the walls become a factor hindering the normal operation of the premises and do not fit well into their interiors. Therefore, various methods of horizontal hidden laying are used.
Piping layout with a branched dead-end scheme.
The minimum pipe lengths and hydraulic resistances of the circuit are leveled by the mutual crossing of pipelines, leading to an increase in the thickness of the screed (each centimeter of it costs from 40 rubles / m2).
- Dead-end scheme with pipelines in the screed or under the plinth.
Piping layout for a two-pipe dead-end system.
The absence of crossing pipes in the scheme is leveled by the need to make holes in the walls (in the above scheme, you need to drill five holes).
- Piping layout according to the scheme with associated water movement (Tichelman scheme).
Piping layout according to the Tichelman scheme.
Here, the first radiator of the heating circuit has the shortest length of the "supply" and the largest length of the "return", the last radiator - vice versa. The hydraulic resistance experienced by the coolant when flowing around the devices of the circuit is constant, which makes it possible to balance any number of radiators in a branch.
Piping layout for a collector-beam system.
The prevalence of this scheme is constantly growing. The pipes here are laid in the floor screed in pairs (“supply” plus “return”), approaching each radiator from the collectors (respectively, “supply” and “return”). The advantage of the scheme is ease of installation (no crossing of pipes and wall holes). The disadvantage is the increased costs due to the large consumption of pipes and additional costs for collectors.
An additional advantage of the beam scheme is the use of pipes of small diameters. An apartment (floor of a private house) will require the use of pipes d = 25 and d = 32 mm for the perimeter wiring diagram. Accordingly, the thickness of the screed, the diameter of the tees that connect the radiators will increase. The cost of such an element is commensurate with the price of a pipe.
The use of beam wiring, which increases the length of the pipes, gives the ultimate benefit by reducing their diameter.
With collector-beam wiring, the method of laying pipes in the floor in a screed is common, the thickness of which is 50-80 mm. Plywood is laid on top, covered with a finishing floor covering (parquet, linoleum). Such a thickness of the screed is quite sufficient for the free "embedding" of the intra-apartment (intra-house) radiant wiring of the heating system.
Connecting radiators with a collector-beam scheme.
Metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene pipes (PEX-pipes) are used, laid in a corrugated pipe or in thermal insulation. PEX pipes have an undoubted advantage here. According to SNiP, only inextricable joints can be “embedded” in concrete. PEX-pipes are connected by means of tension fittings related to inextricable connections.
Even without fittings, not every metal-plastic pipe is uniquely suitable for laying in a floor screed. Manufacturers' products suffer from a serious defect: layers of aluminum and polyethylene delaminate under the influence of repeatedly changing coolant temperature. After all, metal and plastic have different coefficients of volumetric expansion. Therefore, the adhesive connecting them should be:
- internally strong (cohesive);
- adhesive to aluminum and polyethylene;
- flexible;
- elastic;
- heat resistant.
Not all adhesive compositions of even well-known European manufacturers of metal-plastic pipes satisfy these requirements, which delaminate over time, the inner layer of polyethylene in such a pipe “collapses”, reducing its cross section. The normal operation of the system is disrupted, and it is almost impossible to find the location of the malfunction - they usually “sin” for malfunctions of thermostats, pumps and other products with moving parts.

In the light of the foregoing, we recommend that readers pay attention to VALTEC metal-plastic pipes, which use the American DSM adhesive, which ensures the strength of the metal / plastic connection, adhesion and the complete absence of delaminations.
In an apartment with horizontal radiant heating distribution (on the floors of private houses), distribution manifolds (supply and "return") are arranged, collecting all supply and return pipelines at their outlets. They are placed in metal cabinets of a special design, often built into the partitions of bathrooms and opening inside them.
Collector cabinet with heat metering unit.
Collectors can be complete, which are sections of thick pipes with outgoing nozzles, or assembled on tees. These devices can be:
- plastic;
- nickel-plated brass;
- copper;
- stainless steel.
Many well-known manufacturers of heating equipment (VALTEC, etc.) produce ready-made manifold blocks that combine supply and return manifolds, manual adjustment valves (on the supply manifold), thermostatic valves (on the return manifold), automatic air vents, drain valves and mounting brackets.
Complete manifold block.
The task of individual adjustment of the thermal regime of each single-radiator branch of the collector-beam heating system is solved by tuning valves with built-in flow meters. The branches are obtained in different lengths, and the coolant tends to flow in the shortest way with minimal hydraulic resistance. It flows around short branches more intensively, warming up the radiators installed there more strongly.
Adjustment valves on the supply manifold change the flow rate of water (antifreeze), narrowing their conditional passages in short circuits, and expanding in long ones. Setting is a painstaking process, and the setting valve is not designed to quickly shut off or open the coolant flow along the circuits. This function is performed by thermostatic valves.
Thermal valves on the manifold - "return" - these are valves that smoothly shut off the flow manually or automatically. The radiant heating system is easily hydraulically balanced.
Often, not only one heating device is installed in the room, but several. It is irrational to bring a separate two-pipe loop-branch to each radiator with a collector-beam wiring. It is better to lay a separate branch to each room, which will bypass several heating devices indoors, implementing a dead-end or passing scheme.
Scheme of the combined wiring of the heating system.
Such a system is calculated as a beam system. Branches supplying several radiators with coolant are subjected to a separate calculation as dead-end or passing ones. In modern systems, radiators are equipped with thermal valves (thermostats), which are adjusted by users to different temperatures, based on the current requirements for comfort in the room. The stability of the temperature regime in the room becomes difficult to maintain.
It turns out that it is possible to get rid of instability while simultaneously reducing the cost of connecting radiators by connecting them according to the so-called. "through circuit".
"Pass-through" scheme for connecting radiators.
The thermal valve is installed only on the first radiator in the circuit, regulating the coolant flow for all heaters connected in series. They are perceived as one radiator. Difficulties in balancing will arise with multi-section devices (10 or more sections each).
A radiant heating system is the optimal choice of heating method for houses with a large number of rooms and utility rooms or for buildings with several floors. Thanks to its installation, the efficiency of the equipment and the quality of heat transfer are significantly increased, since there are no unnecessary heat losses. In the photo you can see what one of the options for a collector heating scheme for a house looks like.
The principle of operation of the beam wiring is simple, but has a number of features. It implies the location on each floor of several collectors for heating. from which they organize the laying of pipelines for direct and reverse supply of the coolant (in more detail: “Laying of heating pipelines along correct scheme“). If a radial wiring of the heating system is created, the instruction for such a scheme regulates the installation of structural elements in a cement screed.
Radiant heating of a private house is a structure consisting of several main elements:
- heating boiler. This device is the starting point, since from it the hot coolant is directed to pipelines and radiators. The power of the heating unit must correspond to the heat output of the heating equipment. Here there is the following nuance: the beam layout of the heating system, unlike other options for piping, has a greater degree of heat loss, which must certainly be taken into account when calculating the parameters of the equipment.
- Circulation pump. According to the peculiarities of its device, the radiant heating distribution is of a closed type and its operation requires forced circulation of the liquid coolant. For this purpose, a special pump is installed that creates a certain pressure and pumps liquid. As a result, the necessary temperature regime, guaranteeing efficient work heating systems.
- high efficiency of heat carrier distribution;
- the possibility of differentiated regulation of the coolant flow through each circuit up to the complete shutdown of individual circuits or radiators without negative impact to other heating circuits;
- the possibility of automating the process of thermal control of premises, easy integration into systems " Smart House» through the installation of programmable sensors in individual premises;
- obligatory forced circulation of the heat carrier allows to reduce the gap between the temperature of the outlet from the boiler and the "return" heat carrier;
- a well-executed calculation of such a radiant heating scheme using underfloor heating circuits allows you to refuse even the use of radiators.
- heating boiler;
- supply line;
- collector entrance.
Device, advantages and disadvantages of a radiant heating system
The distribution of the heating pipeline must be carried out before the start of internal repair work. If this is not done, then it will be necessary to tear off the screed, lay pipes and re-fill the floors with a special solution.
- on all circuits, the collectors must be equipped with thermostatic valves and devices that regulate the flow of the coolant;
- when implementing the piping scheme for the underfloor heating system, thermostatic heads and electrothermal drives are used. Thanks to these devices, the design of the heated floor immediately responds to changes in the air temperature in the room, maintaining comfort and coziness in it;
- when choosing the type of distribution system, you need to know that it can be made according to a standard or individual scheme. Professionals advise giving preference to the second option. AT individual systems then not only the boiler operates in normal mode, but there are no significant temperature differences, and the fuel is consumed in an economical mode. Underfloor heating, made using an individual beam wiring scheme, can be equipped in any building.
- the ability to hide the laying of the pipeline and other items of equipment;
- lack of connections and, as a result, weak points between the collector and heating radiators;
- simple installation of the system and doing the work yourself, even without special skills. The number of connections is minimal and therefore the assembly is carried out as soon as possible;
- stable operation heating structure. In the case of using the beam method of wiring, there is no possibility of water hammer. especially this problem relevant in the case when it is necessary to install imported plumbing, for which the boundary pressure is 3 atmospheres;
- in order to repair or replace damaged sections of the pipeline, it is enough to turn off the circuit beam, and the entire system will continue to function as before;
- the equipment has an affordable cost, like all its components;
- simplification of the design and installation of the heating structure due to the use of pipes of the same diameter coming from the comb.
The radiant heating system is characterized by efficiency, performance, low price, safety and comfort. Apply this scheme can be in any building for its intended purpose, from your own home to a large office building.
Comfortable life in a warm country house depends not only on the boiler. Everything matters here: from the diameter of the pipes to the heating wiring. The tee system goes into oblivion: too little efficiency and "sluggishness". It is impossible to set the temperature in the rooms at different levels, nor to make repairs in the winter without evicting the household.
Radiant heating system for a private house
4.7 (93.33%) votes: 3The market offers an endless array of heating technologies for those who decide to heat their homes. But the main elements of all systems are the boiler, pipes and heaters that produce space heating.
There are many options for piping connections. Some people prefer a radial (fan) heating system.
Features of beam wiring
All heating systems are produced with one purpose - to heat the room, that is, to restore the heat that is lacking in the house due to the temperature difference inside and outside (outside).
There are only two options for combining all heating devices:
- Trinity connection.
- Beam wiring of the heating system ( collector connection). In this case, a separate pair of pipes is connected to each device with the help of a collector for direct and reverse supply of the heat carrier.
The first version of the pipeline system is budgetary. However, due to the special connection of pipes and connection to one riser, if it is necessary to install a battery or a separate section, the system will have to be turned off entirely and the liquid drained.
Of course, you can also buy stop valves , but the installation will cost much more.
As a rule, the classical distribution of the pipeline around the perimeter is open. Fan heating systems are mainly located in the walls or in the floor, because many pipes lying on the structure do not look very attractive in the interior.
Concealed installation looks good in any room. After all, only heating batteries remain in sight.
The collector-beam heating system is not cheap compared to the perimeter device of the system. However, the advantage of this installation is that the warm liquid will spread to all points at once and evenly heat the rooms.
Collector heating system at home
Pros and cons of a collector heating system
You need to get acquainted with all the advantages and disadvantages of this heating system in advance.
Disadvantages of fan-shaped piping:
- There is only one strong argument against - the beam system has many elements in its design. including pipes. In addition, it uses a lot of connecting elements.
- A large number of parts in this system can be reflected in considerable costs for repair work. A classic heating system costs less and is cheaper to repair.
It is required to take a very responsible approach to connecting all heating devices of the fan circuit, because errors can cause frequent breakdowns of the system as a whole.
Against the background of the advantages of a radiant heating system, the disadvantages lose their weight. Indeed, in the shortest possible time, a well-mounted system will definitely pay for its installation. In addition, it has many useful features.
Advantages:
- The fan system allows you to establish heating separately in each room. Thus, the heat in the premises will be distributed more efficiently, and energy carriers will be saved.
- When installing a radiant heating system, you have access to pipe connections, you can identify and fix problems in time.
- The pipes of a classic heating system are quite difficult to hide. With fan-shaped wiring, the pipes are hidden in the walls or in the field. If the installation is of high quality and correct, then the elements will not be visible to the eye.
A correctly designed scheme of a radiant heating system makes it possible to rationally distribute heat over all areas of the house.
How to make fan wiring
The collector is the most important element of the system under consideration. When is it planned to organize a fan heating system in two-story house, the collector is required to be installed on all floors. Collectors are hidden in a special closet. In the future, they will be easy to maintain or adjust if necessary.
The number of connections is reduced to a minimum, which has a good effect on the hydraulic stability of the entire heating system.
The boiler is the heart of the whole system. To efficiency always strived for the maximum indicator, it is required to take into account the power of the boiler equipment, the consumption of heat energy by heating devices and the heat losses of the system. This applies to all boilers, no matter what type of fuel they operate on.
Some of the heat can be lost with a large length of the pipeline system, which must also be remembered.
Circulation pump selection
Beam piping is usually used in horizontal type systems with a bottom supply of heat carrier. It requires a pump that stimulates the circulation of warm liquid through all branches.
Circulation pump equalizes the temperature readings at the inlet and outlet of the heating circuit. Thus, the quality of heating is improved. The system becomes more compact and less material intensive.
The pump is selected based on performance, as well as head height.
For right choice circulation device in connection with these characteristics, it is necessary to know the diameter of the pipes, their length and distance from the pump itself. It is necessary to calculate these indicators already at the stage of drafting the project.
How to install the pump
To achieve maximum efficiency and quality heating, the following must be taken into account:
- Pumps with wet rotor mounted so that the shaft is horizontal.
- The equipment is usually installed on the return line of the pipeline system, since the temperatures are lower there. Newer devices can also be installed on the supply circuit, they are not afraid of high temperatures.
- Should be as close as possible to expansion tank.
- The thermostatic pump must be kept away from hot objects.
- The heating circuit must be equipped with a de-airing device. In the absence of it, the circulation pump is bought with air vent.
- To remove solids before installation, experts advise flushing the system.
- Before starting the pump, it is worth filling the system with coolant.
In order to avoid noise, it is worth selecting circulating equipment based on the performance of the heating system.
Many are interested in the question of whether it is possible to do without a pump, sensors and air vents. The answer is yes. However, it will be necessary to organize some conditions, because the circulation of the coolant will be natural.
small cottage or other small object may be optimal for a natural circulation system. However, no matter which version of the heating system is chosen, everything should be thought out at the stage of drafting the project.
Distribution header selection
It is also called a comb. It is necessary for supplying liquid to a warm floor, radiators, convectors, etc. With the help of it, an outflow is carried out along the return circuit, from where the liquid is then sent to the boiler or mixed again in the circuit for temperature adjustment. The collector copes with a maximum of twelve branches.
As a rule, combs have redundant locking-regulating and temperature-regulating elements. With the help of them, it is possible to adjust the rational flow of the heat carrier for all heating circuits. The presence of air blowers can guarantee the quality and stability of the system.
Mounting Features
Laying pipes of a hidden type implies the mandatory organization of thermal insulation. Heating elements can be heated up to +90 ° C, which can have a bad effect on both the screed and the wooden elements. You just need a heat-insulating material that restrains the speed heat transfer so that the heat has time to be distributed by the system. The market offers special polyethylene casings for concealed laying of pipelines.
To mount, you will need certain skills. The quality of the prepared pipe (its end with a calibrator) is very important for a tight connection with a fitting. Usually they use reliable compression fittings, connections of branches with fittings on heating batteries and collectors are not made collapsible.
Preparing for installation
Before we start everything installation work, it is worth choosing all the required elements correctly and considering the location of the devices, including the need to:
- Decide on the place of installation of heating batteries.
- Choose the type of radiators in connection with the pressure indicators and the type of heat carrier. Calculate the required number of sections or the area of panel heaters so that there is enough heat to heat all rooms.
- Draw a diagram of heating radiators and laying pipes. Do not forget about other heating elements (boiler, pump and collectors).
- Write down all the necessary elements on paper, and stock up. In order to be sure of the calculations, you can consult with a specialist.
Installation of a radiant heating system
Initially, radiators are installed in each room. Their location on the same level is checked with a level. The power of the devices is calculated based on heat loss. On heating batteries they put plugs, thermostatic head connection points, taps (transition fittings for metal-plastic are connected to them).
Collector box installed. As a rule, simple and cheap distributors are selected, equipped with ball valves with 16 mm outlets and ¾ connections. American women are mounted on the collector.
You can connect the collector device to the boiler (to the tees of the line from the boiler) hidden under the floor or along the walls. Then the collector is connected with a supply and return of 16 mm to all heating devices.
Radiation system and underfloor heating
Fan wiring has the same principle as a water heated floor. Theoretically, a warm floor can be connected with batteries through one comb. This option is suitable in cases where you want to make warm floors in certain rooms, and install batteries in others.
When planning a fan distribution with warm floors remember that the system will work, however the floor heating is a low temperature system and the radiators require high temperatures.
When nothing can be done to adjust the temperature, then there are two options: either with warm floors in the room you will be stuffy, or with batteries it will be cold. Remember this.
I must say about another plus of the collector heating system - a comfortable warm floor. This is because when fan-shaped wiring is installed, the distributors are placed near the risers or the center of the room. For all that, the pipes from the distributor to the batteries most often pass along the corridors, entering the premises through the door openings.
Pipelines are insulated with a material in one layer. However, most craftsmen know that 6-9 mm thermal insulation transmits up to 30% of heat.
Therefore, in places where the radiant heating system passes, the floors are not cool, but warm. The benefit is twofold: a reliable heating system without joints and optimally warm underfloor heating.
In a wooden house
To lay the pipeline in the base of wood, you need to make holes in wooden beams overlap. With all the holes, you need to make a little more than the diameter of the pipes in order to exclude the pressure of the beam on the structure.
It is required to securely fasten the pipes in wooden floors but not create pressure.
Connections should be above the floor covering, they should not be in the thickness of the floor.
Frequently asked Questions
- Q: What pipe diameter is best?
Answer: as practice shows, the 16th pipe diameter is enough to install the fan system. Rarely use a larger size. - Question: Is it possible to have a radiant heating system for a private house with two floors?
Answer: of course. Wiring can be arranged in a three- and four-story house. It is only important to put a separate collector on each floor. - Question: is fan wiring possible in the apartment?
Answer: it's real. Most likely, this cannot be done directly from the combined heat and power plant. But if you have your own heating system, or if you connect to the combined heat and power plant through a heat exchanger, then everything will work.
If we consider the radiant heating system at home in more detail, we can highlight even more of its advantages than mentioned above. Analyzing them, you can close your eyes to the shortcomings. Of course, an efficient system with high performance simply cannot be cheap, but its long life and easy maintenance are trustworthy.
Being a variety of methods for laying heating pipes of two-pipe horizontal systems of modern apartment buildings and private houses, beam wiring of the heating system has a number of undeniable advantages. Each circuit of the system with such piping is separately connected to the heating manifold, which allows you to set an individual operating mode for it that meets the criterion of comfort for a person in a particular area of \u200b\u200bthe room.
Heating pipes laid in the thickness of a concrete screed or under a wooden floor on logs must be reliable, excluding (or minimizing) the likelihood of leaks, deterioration in throughput and other malfunctions.
Wiring diagrams of modern horizontal heating systems
Modern multi-apartment residential buildings and private cottages of any number of storeys are increasingly equipped with horizontal heating systems. A necessary element of such a scheme is one or more (in an apartment building - in each entrance) vertical two-pipe risers with branches / inputs to separate rooms / apartments on each floor. Further laying of pipelines is carried out in a "horizontal" way.
Arranging such systems, builders invariably face the problem of the difficulty of laying heating pipes to radiators. The pipelines of vertical systems, laid along the walls from top to bottom, did not particularly interfere with the residents. Horizontal pipes laid openly along the walls become a factor hindering the normal operation of the premises and do not fit well into their interiors. Therefore, various methods of horizontal hidden laying are used.
Branched dead-end wiring diagram with pipes in the screed
The minimum pipe lengths and hydraulic resistances of the circuit are leveled by the mutual crossing of pipelines, leading to an increase in the thickness of the screed (each centimeter of it costs from 40 rubles / m2).
Perimeter wiring of the heating system
- Dead-end scheme with pipelines in the screed or under the plinth.

The absence of crossing pipes in the scheme is leveled by the need to make holes in the walls (in the above scheme, you need to drill five holes).
- Piping layout according to the scheme with associated water movement (Tichelman scheme).

Here, the first radiator of the heating circuit has the shortest length of the "supply" and the largest length of the "return", the last radiator - vice versa. The hydraulic resistance experienced by the coolant when flowing around the devices of the circuit is constant, which makes it possible to balance any number of radiators in a branch.
Collector-beam wiring of the heating system

The prevalence of this scheme is constantly growing. The pipes here are laid in the floor screed in pairs (“supply” plus “return”), approaching each radiator from the collectors (respectively, “supply” and “return”). The advantage of the scheme is ease of installation (no crossing of pipes and wall holes). The disadvantage is the increased costs due to the large consumption of pipes and additional costs for collectors.
An additional advantage of the beam scheme is the use of pipes of small diameters. An apartment (floor of a private house) will require the use of pipes d = 25 and d = 32 mm for the perimeter wiring diagram. Accordingly, the thickness of the screed, the diameter of the tees that connect the radiators will increase. The cost of such an element is commensurate with the price of a pipe.
The use of beam wiring, which increases the length of the pipes, gives the ultimate benefit by reducing their diameter.
General requirements for the installation of beam wiring
With collector-beam wiring, the method of laying pipes in the floor in a screed is common, the thickness of which is 50-80 mm. Plywood is laid on top, covered with a finishing floor covering (parquet, linoleum). Such a thickness of the screed is quite sufficient for the free "embedding" of the intra-apartment (intra-house) radiant wiring of the heating system. It is possible to lay pipes outside along the walls under decorative plinths, which inevitably increases the length of the pipelines. Known options for laying pipes for beam wiring in the space of a false (suspended) ceiling, in strobes.

Metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene pipes (PEX-pipes) are used, laid in a corrugated pipe or in thermal insulation. PEX pipes have an undoubted advantage here. According to SNiP, only inextricable joints can be “embedded” in concrete. PEX-pipes are connected by means of tension fittings related to inextricable connections. Metal-plastic pipes use compression fittings with union nuts. To “monolichize” them means to violate the SNiP. Each detachable pipe connection must be accessible for maintenance (tightening).
Even without fittings, not every metal-plastic pipe is uniquely suitable for laying in a floor screed. Manufacturers' products suffer from a serious defect: layers of aluminum and polyethylene delaminate under the influence of repeatedly changing coolant temperature. After all, metal and plastic have different coefficients of volumetric expansion. Therefore, the adhesive connecting them should be:
- internally strong (cohesive);
- adhesive to aluminum and polyethylene;
- flexible;
- elastic;
- heat resistant.
Not all adhesive compositions of even well-known European manufacturers of metal-plastic pipes satisfy these requirements, which delaminate over time, the inner layer of polyethylene in such a pipe “collapses”, reducing its cross section. The normal operation of the system is disrupted, and it is almost impossible to find the location of the malfunction - they usually “sin” for malfunctions of thermostats, pumps and other products with moving parts.
In the light of the foregoing, we recommend that readers pay attention to VALTEC metal-plastic pipes, which use the American DSM adhesive, which ensures the strength of the metal / plastic connection, adhesion and the complete absence of delaminations.
Collector cabinets and blocks
In an apartment with horizontal radiant heating distribution (on the floors of private houses), distribution manifolds (supply and "return") are arranged, collecting all supply and return pipelines at their outlets. They are placed in metal cabinets of a special design, often built into the partitions of bathrooms and opening inside them. It is also possible to install distribution manifolds in specially arranged wall niches. Often, the collector unit is combined with the heat metering unit in one collector cabinet.

Collectors can be complete, which are sections of thick pipes with outgoing nozzles, or assembled on tees. These devices can be:
- plastic;
- nickel-plated brass;
- copper;
- stainless steel.
Many well-known manufacturers of heating equipment (VALTEC, etc.) produce ready-made manifold blocks that combine supply and return manifolds, manual adjustment valves (on the supply manifold), thermostatic valves (on the return manifold), automatic air vents, drain valves and mounting brackets.

The task of individual adjustment of the thermal regime of each single-radiator branch of the collector-beam heating system is solved by tuning valves with built-in flow meters. The branches are obtained in different lengths, and the coolant tends to flow in the shortest way with minimal hydraulic resistance. It flows around short branches more intensively, warming up the radiators installed there more strongly.
Adjustment valves on the supply manifold change the flow rate of water (antifreeze), narrowing their conditional passages in short circuits, and expanding in long ones. Setting is a painstaking process, and the setting valve is not designed to quickly shut off or open the coolant flow along the circuits. This function is performed by thermostatic valves.
Thermal valves on the manifold - "return" - these are valves that smoothly shut off the flow manually or automatically. The radiant heating system is easily hydraulically balanced.
Combined heating piping layout
Often, not only one heating device is installed in the room, but several. It is irrational to bring a separate two-pipe loop-branch to each radiator with a collector-beam wiring. It is better to lay a separate branch to each room, which will bypass several heating devices indoors, implementing a dead-end or passing scheme.

Such a system is calculated as a beam system. Branches supplying several radiators with coolant are subjected to a separate calculation as dead-end or passing ones. In modern systems, radiators are equipped with thermal valves (thermostats), which are adjusted by users to different temperatures, based on the current requirements for comfort in the room. The stability of the temperature regime in the room becomes difficult to maintain.
It turns out that it is possible to get rid of instability while simultaneously reducing the cost of connecting radiators by connecting them according to the so-called. "through circuit".

The thermal valve is installed only on the first radiator in the circuit, regulating the coolant flow for all heaters connected in series. They are perceived as one radiator. Difficulties in balancing will arise with multi-section devices (10 or more sections each).
Automatic collector-beam system
The supply of coolant to radiators connected by beam wiring can be made automatically adjustable. In this case, a small-sized electromechanical servo drive is installed on the return manifold thermal valves (item 2 in the figure "Complete manifold block") instead of the plastic cover for manual control (position 4 in the figure "Complete manifold block"), connected by a cable to an analog thermostat or controller. Radiators are connected to heating pipes without fittings at all (ball valves can be installed).

Such a scheme has an increased capital cost, while providing an increased level of comfort. the air temperature desired by the user can be set from the control panel of the room thermostat, the signals of which are processed by servomotors on the thermal valves of the “return” collector. The system can be controlled by the so-called chrono-thermostat, which provides the user with the opportunity to set a temperature control program for a week with differentiation by day of the week and time of day.
Conclusion
The heating system with collector-beam piping provides the user with the possibility of hydraulic balancing and individual adjustment of the operating modes of heating devices. Some increase in the length of the pipes with beam wiring is obviously compensated by a decrease in their diameter and ease of installation.
There is a fairly large variety of autonomous heating systems that are designed to heat private houses. In places where there are regular power outages or there is no gas main nearby, people prefer traditional Russian stoves. This is the most striking example of a radiant heating system for a private house.
Modern radiant heating
Distribution of a radiant heating system
Russian ovens have quite big sizes, which sometimes creates difficulties in their installation in country houses and even more so in city apartments. However, technology does not stand still, heating systems are modified and adapted to the needs of modern man.
According to the piping from the collector to the radiators, the systems are divided into three types:
- radiation;
- two-pipe;
- single-pipe.
The principle of operation of radiant heating is based on the fact that the wiring is meant separately for each radiator. This is the most significant advantage of this system. If necessary, radiators can be turned on and off as groups or individually.
The system is equipped with a special heat supply valve. If it is warm outside or household appliances are working in the kitchen, the valve can be screwed a little. Thanks to the ability to regulate the supply of heat to the rooms, it is possible to save fuel.
Features and segments of beam wiring

Elements of a radiant heating system
A radiant heating system is most suitable for use in apartment buildings or country/private homes with multiple floors and many rooms. This allows you to increase the efficiency of the entire heating system, guarantees high-quality heat supply and will economically require a resource.
The principle of operation of a radiant heating system is simple, but has its own characteristics. If the structure has several floors, collectors must be installed on each. Moreover, in some cases it is advisable to install not one, but several collectors on the floor, and pipe pipes from them. The effectiveness of the equipment will be undeniable if the house is well insulated and heat loss is minimal.
The radiant heating system includes several basic elements necessary for high-quality work.
- The boiler is the main part. From it heat is supplied to the pipes, and from there to the radiators.
- Circular pumping station, thanks to which the necessary pressure is provided in the pipes and the coolant circulates.
- A collector with the help of which a uniform supply and distribution of heat throughout all rooms is carried out.
Another component is the closet. It manages to hide the distribution manifold, valves and pipes. The design is simple, practical and functional.
Beam heating connection diagram

Circulation pump connection diagram
In search of the most optimal type of heating scheme, most often preference is given to radial floor-by-floor piping. The essence of the method lies in the fact that all pipes and components are hidden in the thickness of the floor. The main distribution body of the system is mounted in a niche of a wall fence or in a special cabinet.
To implement the connection scheme, you need a circular pump or several devices that are mounted on each branch or ring. Most often, this scheme is implemented on the basis of one- and two-pipe installation, displacing the tee connection method.
A supply and return manifolds are installed near the riser of a two-pipe system. From them, pipes are run under the floors to each radiator installed on the floor.
Each of the contours should approximately have the same length. If for some reason this cannot be realized, the large circuit must be separately equipped with a circulation pump, automatic temperature control.
In this case, the temperature indicators on each circuit will be independent of each other. This is due to the fact that the pipeline will be under the screed. Each radiator is additionally equipped with an air valve. Air vents are usually installed on the manifold.
Before starting work, you need to determine the location of the equipment, make a paper list of everything you need and schematically depict the location of the selected radiators.
Radiant heating system and underfloor heating
A radiant heating system and a water heated floor are mounted in a similar way. Underfloor heating can be connected to radiators through one manifold. This approach is extremely popular among people who want to insulate floors in some rooms, and not throughout the living space.
It is extremely important to provide for temperature control, otherwise the room may be too hot or cold. When organizing a warm floor, pipes must be insulated in one layer. Insulating material 6-10 mm thick transmits no more than 30% of heat.
Advantages and disadvantages

With radiant heating, all radiators receive a coolant with the same temperature.
The collector-beam heating system has absorbed all the advantages of its predecessors, which is the reason for the popularity of the equipment.
Main advantages:
- Aesthetics.
- In terms of hydraulics, this is the most advanced heating system. Individual lines are drawn to each battery, so the system segments are independent.
- If desired or necessary, you can disconnect any battery.
- All radiators receive water at the same temperature.
- It is possible to equip the system with means of automatic regulation and control of the entire circuit as a whole.
- The minimum number of connections, there are no tees.
The most significant drawback is the high cost of equipment and its installation. The cost of expensive manifolds and increased piping footage cannot compensate for the lack of fittings. If the building has several floors, the cost of equipment doubles, triples, etc., depending on the number of floors. The installation itself under the floors in the future involves additional work on the installation of flooring.
Modernization of any beam system is not particularly difficult; its implementation will require the installation of additional valves with a thermostatic head on each radiator that is connected to the system. Thanks to the thermostat, it is possible to set the most optimal temperature regime in a particular case. The temperature will not rise above the parameters set by the person.
It is advisable to modernize the heating system in those buildings where each room is delimited according to its purpose. For example, one temperature range is needed to store goods, and another is needed for a comfortable stay in a room for people.
In the search for the most suitable heating system, it usually turns out that it is the radiant system that is best suited, since it has much more advantages than disadvantages. The latter rest only on finances, while the efficiency and performance of the system is at its best. The average life of heating equipment is 50 years.
